3D printing basics – Additive vs. Subtractive
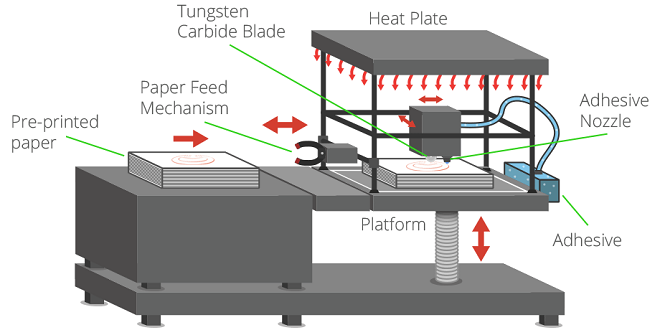
3D printing has been one of the most innovative pieces of technology that has been commercialized over the past decade. It promises lots of change, from sustainable building and manufacturing processes to changes in hobbies like model making. Some of the most remarkable projects in the world exceed expectations. But there are many exciting home projects too. There are two key concepts that will change 3D printing.
Subtractive Printing
Subtractive 3D printing, as the name suggests, is the act that removes material to create an end product. For older devices, this might have been the act to start with a larger block and work out the plan for how to remove it. While many modern printers now work on the additive process, it remains an integral part of larger projects. It also plays a part in smaller scale printing.
Additive Printing –
Instead of building layers of material to reach the final product, this process requires a larger spool that is slowly fed through. This is how the project is built. Although this can be slow for larger projects, it has revolutionized how some processes take place. However, the slower process can be quite cheap, with the energy cost being the defining element for many. This has led to changes in expectations for larger projects.
Both can be used in the manufacturing process for various purposes. However, finished products may still come from a subtractive method, whether it’s through 3D printing machines, or more likely through CNC options. This is especially true for larger volumes where speed is important. But, more complex parts or parts that require weight savings or intricate designs, are best suited for additive manufacturing. 3D printing shines because speed isn’t always a factor.
If you are interested in home-based manufacturing, it is worth looking into both the process and whether or not it is more manageable.
The Women Delusion Calculator is constantly evolving with advanced features. Future developments will focus on enhancing user experience. Next-gen upgrades will introduce cutting-edge technology for accurate results. The calculator is expanding its scope to include other demographics, catering to a wider audience.
